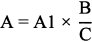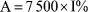Motor Accidents (Liabilities and Compensation) Regulations 2020
I, the Governor in and over the State of Tasmania and its Dependencies in the Commonwealth of Australia, acting with the advice of the Executive Council, make the following regulations under the Motor Accidents (Liabilities and Compensation) Act 1973 .
28 January 2020C. WARNER
Governor
By Her Excellency's Command,
MICHAEL DARREL JOSEPH FERGUSON
Minister for Infrastructure and Transport
These regulations may be cited as the Motor Accidents (Liabilities and Compensation) Regulations 2020 .
These regulations take effect on 17 February 2020.
In these regulations –Act means the Motor Accidents (Liabilities and Compensation) Act 1973 ;certificate of premium paid means a certificate issued by the Registrar on receipt of a premium paid in respect of a motor vehicle specified in that certificate.
4. Certificate of premium paid
(1) If a person pays a premium payable in respect of a vehicle under section 30 of the Act, the Registrar is to issue a certificate of premium paid to the registered operator of the vehicle.(2) A certificate of premium paid issued under subregulation (1) in respect of a vehicle remains in force –(a) in the case of a registered motor vehicle, for the same period for which the premium in respect of that vehicle has been paid; or(b) in the case of an unregistered motor vehicle, for the same period for which registration is sought in respect of that vehicle commencing –(i) on the date of payment of the first premium; or(ii) if a premium is paid within 28 days of the expiration of the immediately preceding period for which a certificate of premium paid was in force, on the expiration of that preceding period; or(iii) if a premium is paid more than 28 days after the expiration of that preceding period, on the date of payment of the premium.
5. Records relating to premiums
(1) In this regulation –class has the same meaning as in the Economic Regulator (MAIB Premiums) Order 2017 .(2) For the purposes of section 33(4)(e) of the Act, the class of a motor vehicle for which the premium is paid is a particular that is required to be recorded.(3) The Registrar –(a) may keep a record under section 33(4) of the Act electronically; and(b) is to provide a copy of records kept under section 33(4) of the Act to the Board.
6. Extract of records as evidence
(1) An extract of a record made, or kept, under section 33(4) of the Act and certified under subregulation (2) is evidence of the facts contained in that extract.(2) For the purposes of subregulation (1) , an extract of the records may be certified by –(a) the chief executive officer of the Board; or(b) an officer of the Board authorised by the Board for that purpose; or(c) the Registrar or a person authorised by the Registrar to give the certification on the Registrar's behalf.
7. Refund of premium on surrender of registration
(1) On acceptance of an application for the surrender of the registration of a registered motor vehicle under the Vehicle and Traffic Act 1999 , the Registrar is to make a refund to the former registered operator of the vehicle, of a premium paid in accordance with section 30 of the Act in relation to the vehicle, calculated in accordance with the following formula:where –A is the amount of the refund;A1 is the amount of the premium paid;B is the number of days remaining in the period in respect of which the premium was paid as at the date of acceptance of the application for the surrender of registration;C is the total number of days in the period that the premium was to be in force.(2) The Registrar may deduct from the amount of the refund a reasonable administrative fee for making the refund and no refund is to be made if the amount of the refund does not exceed the amount of the fee.
8. Registrar to remit amounts to Board
The Registrar is to remit to the Board an amount equal to all premiums received by the Registrar on behalf of the Board, less any refunds made under regulation 7 .
The following are prescribed as a jurisdiction to which section 20 of the Act applies:(a) Australian Capital Territory;(b) New South Wales;(c) Northern Territory;(d) Queensland;(e) South Australia;(f) Victoria;(g) Western Australia.
(1) The benefits payable under section 23(1) , (1A) or (2) of the Act by the Board in respect of a matter are the benefits specified in Schedule 1 for that matter.(2) A person may make a claim for benefits payable under section 23(1) , (1A) or (2) of the Act in respect of a motor accident if –(a) within one year after the date of the motor accident, written notice of the personal injury giving rise to the claim is given to the Board; and(b) the claim is brought within one year after –(i) the date of death resulting directly from the motor accident; or(ii) the date on which loss or expense resulting directly from the motor accident was incurred; or(iii) the date on which gratuitous care required as a direct result of the motor accident was, or services care required as a direct result of the motor accident were, provided.(3) On application by the person making the claim and after hearing such evidence as it considers appropriate, the Tribunal may extend a period referred to in subregulation (2) by such period not exceeding 5 years as it thinks fit.(4) The Tribunal may extend either period referred to in subregulation (2) even though one or both of the periods has expired.
(1) In this regulation –agricultural implement means an implement that is built to –(a) be towed by a motor vehicle; and(b) perform agricultural tasks;[Regulation 11 Subregulation (1) amended by S.R. 2021, No. 30, Applied:01 Jun 2021] agricultural machine means an agricultural machine as defined in the Vehicle and Traffic (Driver Licensing and Vehicle Registration) Regulations 2021 .(2) For the purposes of section 29(1AA) of the Act, the following kinds of trailer are prescribed:(a) a trailer, other than a caravan, with an unladen mass of not more than half a tonne;(b) an agricultural implement towed by another motor vehicle;(c) a trailer towed by an agricultural machine while the agricultural machine is performing agricultural tasks.
SCHEDULE 1 - Scheduled Benefits
PART 1 - Preliminary
1. Interpretation of ScheduleIn this Schedule –2007 release day means the day in May 2007 on which the adult average weekly earnings for the February 2007 quarter were published by the Australian Bureau of Statistics;child of a marriage or significant relationship – see clause 2 ;child, of a person, includes a child legally adopted by that person but does not include a biological child of that person if the person is no longer the lawful parent of that biological child;counselling services has the same meaning as in section 23 of the Act;dependant, of a person whose death results directly from a motor accident, means each of the following:(a) an individual who is the spouse of the person and who, but for the death of the person, would be wholly or partly dependent on the person for financial support;(b) an individual who –(i) is the parent or step-parent of a dependent child, being a dependent child who, but for the death of the person, would be wholly or partly dependent on the person for care; and(ii) is the spouse of the person;(c) a dependent child of the person;(d) a dependent parent of the person;(e) a dependent carer of the person;dependent carer – see clause 6 ;dependent child, of a person, means –(a) an individual who –(i) is, or, but for the personal injury of the person, would be, wholly or partly dependent on the person for financial support; and(ii) is a child of the person or is a child of a marriage, or significant relationship, to which the person is a party; and(iii) does not have a spouse; and(iv) either –(a) is less than 16 years of age; or(b) has attained 16 years of age but is less than 25 years of age and is a full-time student; or(b) an individual who –(i) is, or, but for the personal injury of the person, would be, wholly or partly dependent on the person for care other than financial support; and(ii) is a child of the person or is a child of a marriage, or significant relationship, to which the person is a party; and(iii) is less than 16 years of age;dependent parent – see clause 5 ;family member has the same meaning as in section 23 of the Act;registered, in relation to a person, means –(a) in the case of a chiropractor, dentist, osteopath, physiotherapist or psychologist, that the person is registered in the relevant health profession under the Health Practitioner Regulation National Law (Tasmania) ; or(b) in the case of a naturopath, that the person is registered by the Australian Register of Naturopaths and Herbalists Limited [ABN 42 147 439 469], or holds such other qualification as determined by the Board; or(c) in the case of a massage therapist, the person is a member of the Australian Association of Massage Therapists Limited [ABN 70 104 153 460] or holds such other qualification as determined by the Board;significant relationship has the same meaning as in the Relationships Act 2003 ;spouse, in relation to a person involved in a motor accident, includes a person who, at the time of the motor accident, is in a significant relationship with that person.
2. Child of a marriage or significant relationship(1) For the purposes of this Schedule, a person is a child of a marriage or significant relationship if the person is –(a) a child of both parties to the marriage or significant relationship; or(b) a child of either party to the marriage or significant relationship and is accepted as a child of the marriage or significant relationship by the other party.(2) For the purposes of subclause (1)(b) , unless the contrary is shown, a child of either party to a marriage or significant relationship is accepted by the other party to the marriage or significant relationship if the child is a member of the parties' household.
3. Paternity(1) For the purposes of this Schedule, a person is the father of another person if –(a) the person has acknowledged, in writing or by a course of conduct, that he is the father of the other person; or(b) a court in this State or elsewhere has made an order or other determination in relation to the maintenance or custody of the other person or a determination that the person is the father of the other person; or(c) the person has been declared under the Status of Children Act 1974 to be the father of the other person.(2) For the purposes of this Schedule, a person is to be taken to have no surviving father if there is no person acknowledged, determined or declared, under subclause (1) , to be his or her father.
4. Unborn childFor the purposes of this Schedule, if a woman was pregnant at the time of a motor accident, these regulations apply to a child born from that pregnancy as if the child –(a) had been born immediately before the accident; and(b) had been dependent on both parents, or whichever parent as was then living, for financial support at the time of the accident.
5. Dependent parentFor the purposes of this Schedule, a person is a dependent parent of another person if the person –(a) is a parent of the other person; and(b) ordinarily resides with the other person at the same premises; and(c) is principally dependent on the other person for financial support.
6. Dependent carerFor the purposes of this Schedule, a person is a dependent carer of another person if the person –(a) is in a caring relationship, within the meaning of the Relationships Act 2003 , with the other person; and(b) ordinarily resides with the other person at the same premises; and(c) is principally dependent on the other person for financial support.
7. SurvivorshipFor the purposes of this Schedule –(a) subject to paragraph (b) , a person survives another person only if the person is living at the end of a period of 30 days beginning on the day on which the other person dies; and(b) a child born after the death of a person survives that person only if the child is living at the end of a period of 30 days beginning on the day on which the child is born.
8. Limitation of amount of medical and disability benefitsExcept in the case of a person requiring daily care, the payment of medical benefits under Part 2 and disability benefits under Part 6 in respect of a personal injury to a person resulting directly from a single motor accident is not to exceed –(a) if the person has been a continuous hospital in-patient for more than 4 days commencing on the date of the accident, $500 000 in aggregate; or(b) in any other case, $400 000 in aggregate.
PART 2 - Medical benefits
1. Medical benefits(1) Subject to this Part, if a person suffers personal injury resulting directly from a motor accident, all the expenses reasonably and necessarily incurred by the person, or on his or her behalf, for the provision of treatment required by him or her within the Commonwealth as a result of the injury are payable as medical benefits.(2) If any sums are paid, or required to be paid, under a law of the Commonwealth in respect of the provision of any treatment referred to in subclause (1) , any amount payable under that subclause in respect of the provision of that treatment is to be reduced by the amount of those sums.(3) In relation to a person who has suffered personal injury, the treatment referred to in this clause includes the following:(a) medical or surgical treatment by, or under the supervision of, a medical practitioner;(b) therapeutic treatment obtained at the direction of a medical practitioner;(c) psychological services provided by, or under the supervision of, a registered psychologist;(d) dental treatment by, or under the supervision of, a registered dentist;(e) therapeutic treatment by, or under the supervision of, one or more of the following people –(i) a registered chiropractor; or(ii) a registered massage therapist; or(iii) a registered naturopath; or(iv) a registered osteopath; or(v) a registered physiotherapist;(f) an examination, test or analysis carried out on, or in relation to, an injured person at the request or direction of a medical practitioner, registered dentist or registered psychologist and the provision of a report in respect of such an examination, test or analysis;(g) treatment and maintenance as a patient at a hospital;(h) road accident rescue services and ambulance services;(i) nursing care, rehabilitation services and the provision of medicine, medical supplies, surgical supplies and any apparatus associated with such care or services, whether in hospital or otherwise;(j) travel by taxi for the purpose of obtaining treatment from a person determined by the Board if –(i) the distance travelled is 20 kilometres or less one way; and(ii) the travel occurs within 39 weeks after the date on which the personal injury was sustained; and(iii) a medical practitioner certifies that, by reason of the injury, the person who has suffered the injury requires a taxi for the purpose of travel;(k) travel by any means for the purpose of obtaining treatment from a person determined by the Board if –(i) the person who has suffered the personal injury requires daily care; or(ii) the distance travelled is greater than 20 kilometres one way.(4) For the purposes of this clause, the expense of providing treatment for any person is taken to be –(a) unreasonably incurred to the extent to which it exceeds the expense that would be incurred if that treatment had been provided in the most economical manner practicable in the circumstances; and(b) unnecessarily incurred if the treatment is not warranted, beneficial to the person and curative of the person's injury.
PART 3 - Funeral benefits
1. Funeral benefitsSubject to clause 2 , if the death of a person results directly from a motor accident, all expenses reasonably incurred in the burial or cremation of the body are payable as funeral benefits, other than expenses incurred in the provision or erection of a gravestone for the person.
2. Limitation on funeral benefits(1) The maximum amount payable under clause 1 of this Part in respect of a motor accident that occurs on or after 1 December 2007 is $7 500, plus an additional amount calculated in accordance with the following formula:where –A is the additional amount payable in dollars;I% is the total percentage increase in adult average weekly earnings between the adult average weekly earnings released on the 2007 release day and the most recently released adult average weekly earnings for the period ending in May.(2) The maximum amount payable as funeral benefits in respect of a motor accident that occurred before 1 December 2007 is to be determined in accordance with the Motor Accidents (Liabilities and Compensation) Regulations 2000 as in force immediately before 1 December 2007.
PART 4 - Death benefits
1. Benefits on death of person with dependants(1) If the death of a person results directly from a motor accident and the person is survived by one or more dependants, a lump sum is payable as death benefits.(2) Subject to this Part, the lump sum payable under subclause (1) in respect of a motor accident that occurs on or after 17 February 2020 is a sum of $88 000.(3) If the deceased is survived by 2 or more dependants, of whom at least one is a dependent child who –(a) is less than 9 years of age, the lump sum specified under subclause (2) is to be increased by $26 000 in respect of each such dependent child; or(b) has attained 9 years of age but is less than 18 years of age, the lump sum specified under subclause (2) is to be increased by $13 000 in respect of each such dependent child; or(c) has attained 18 years of age but is less than 25 years of age, the lump sum specified under subclause (2) is to be increased by $5 200 in respect of each such dependent child.(4) The lump sum payable as death benefits under this clause is –(a) payable to the dependants of the deceased; and(b) to be apportioned between the dependants as the Board considers appropriate having regard to the degree of dependency of each dependant; and(c) in the case of a lump sum payable to a dependent child under 18 years of age, to be paid to the Public Trustee on behalf of that child.(5) The lump sum payable as death benefits in respect of a motor accident that occurred on or after 1 August 2012 but before 17 February 2020 is to be determined in accordance with the Motor Accidents (Liabilities and Compensation) Regulations 2010 as in force immediately before 17 February 2020.(6) The lump sum payable as death benefits in respect of a motor accident that occurred on or after 1 March 2010 but before 1 August 2012 is to be determined in accordance with the Motor Accidents (Liabilities and Compensation) Regulations 2000 as in force immediately before 1 August 2012.(7) The lump sum payable as death benefits in respect of a motor accident that occurred on or after 1 December 2007 but before 1 March 2010 is to be determined in accordance with the Motor Accidents (Liabilities and Compensation) Regulations 2000 as in force immediately before 1 March 2010.(8) The lump sum payable as death benefits in respect of a motor accident that occurred before 1 December 2007 is to be determined in accordance with Motor Accidents (Liabilities and Compensation) Regulations 2000 as in force immediately before 1 December 2007.
2. Effect of disability allowanceIf a person has received payments under Part 5 by way of disability allowance in respect of personal injury resulting directly from a motor accident, any lump sum otherwise payable by way of death benefits in respect of that person's death is to be reduced by the amount of disability allowance paid.
PART 5 - Disability allowances
1. Interpretation of Part(1) For the purposes of this Part –(a) the holding of an office of profit is taken to constitute employment; and(b) in relation to any such office, a reference in this Part to anything done by an employer is to be construed as including a reference to anything done in relation to that office by a person having authority in relation to that office to exercise the powers ordinarily exercisable by a person in relation to other persons in that person's employment.(2) In this Part, a reference to remuneration is to be construed as a reference to an emolument of any kind.(3) In this Part –earnings, in respect of a person who has suffered personal injury, does not include an amount that is required to be paid in respect of the person by the person's employer –(a) as a contribution to a superannuation fund in accordance with the Superannuation Guarantee (Administration) Act 1992 of the Commonwealth; or(b) to a defined benefits scheme of a superannuation fund.
2. Types of disability allowances(1) In accordance with this Part, periodical allowances are payable as disability allowances to any person who suffers personal injuries resulting directly from a motor accident.(2) A disability allowance may be –(a) an employed person's allowance; or(b) a self-employed person's replacement allowance; or(c) a housekeeping allowance.(3) Unless provided to the contrary in this Part, a person is not entitled to both an employed person's allowance and a self-employed person's replacement allowance.
3. Employed person’s allowance(1) For the purposes of this clause –prescribed period means a period of 156 weeks beginning at the expiration of the period referred to in subclause (4)(a) .(2) A person who suffers personal injury is entitled to an employed person's allowance if, at the time of the motor accident –(a) the injured person was engaged in employment or an occupation for remuneration or profit; or(b) the injured person was travelling directly from his or her place of residence to the place at which, upon arrival at the end of the journey in the course of which the accident occurred, he or she was to take up employment or an occupation for remuneration or profit; or(c) the injured person –(i) was, on the day of the accident, at least 15 years old or exempt from the requirement to attend school under a law of the State; and(ii) had been engaged in employment or an occupation for remuneration or profit for a total period of not less than 26 weeks in the 12 months immediately preceding the day of the accident; and(iii) was actively seeking employment through all avenues reasonably available to him or her, or was certified by a medical practitioner as unfit for work due to injury or illness.(3) For the purposes of subclause (2) , a person engaged in employment or an occupation is to be treated as continuing to be so engaged notwithstanding the person's temporary absence, with leave of his or her employer or otherwise, or the person's temporary standing down from employment by his or her employer.(4) An employed person's allowance is payable –(a) for such periods, falling within the period of 104 weeks beginning on the day of the motor accident, during which the injured person is wholly disabled from engaging in his or her usual employment or occupation as a consequence of the injury; and(b) for such other periods, falling within the prescribed period, during which the injured person is, by reason of the injury, wholly disabled from engaging in any employment or occupation for which he or she would otherwise be reasonably suited by education, training, experience or ability.(5) If the average weekly earnings of the injured person exceed $400 per week, the employed person's allowance is payable at the lesser of the following rates:(a) 80% of his or her average weekly earnings;(b) 3 times the adult average weekly earnings as last published before the motor accident occurred.(6) If, at the time of the motor accident, the injured person's average weekly earnings did not exceed $400 per week, whether or not the person was a dependant of another person, the lesser of the following amounts is payable weekly as the employed person's allowance:(a) $320;(b) the injured person's average weekly earnings.(7) If, in respect of any period during which an employed person's allowance would, apart from this subclause, be payable to a person, that person receives remuneration or profit from any employment or occupation –(a) the amount of that allowance is to be reduced by the amount of that remuneration or profit; and(b) if the amount of that remuneration or profit exceeds the amount of the allowance, the allowance is not payable in respect of that period.
4. Self-employed person's replacement allowance(1) For the purposes of this clause –business includes any profession, trade, employment, vocation and calling, but does not include an occupation as an employee;prescribed period means a period of 156 weeks beginning at the expiration of the period referred to in subclause (3)(a) .(2) A person who suffers personal injury is entitled to a self-employed person's replacement allowance if –(a) at the time of the motor accident he or she was carrying on a business for profit; and(b) he or she is disabled from conducting that business as a result of the injury and, to ensure that the business is carried on during the period in which he or she is so disabled, arrangements are made for another person to receive remuneration, gratuity or reward to conduct that business.(3) A self-employed person's replacement allowance is payable –(a) for such periods, falling within the period of 104 weeks beginning on the day of the motor accident, during which the injured person is wholly disabled from conducting his or her business as a result of the injury and arrangements are made for another person to receive remuneration, gratuity or reward to conduct that business; and(b) for such other periods, falling within the prescribed period, during which the injured person is, by reason of the injury, wholly disabled from engaging in any employment or occupation for which he or she would otherwise be reasonably suited by education, training, experience or ability.(4) Subject to subclause (5) , a self-employed person's replacement allowance is payable at the lesser of the following rates:(a) 80% of any remuneration, gratuity or reward paid to a person to carry on a self-employed person's business;(b) 3 times the adult average weekly earnings as last published before the motor accident occurred.(5) If a self-employed person returns to his or her business in a reduced capacity, the amount of self-employed person's replacement allowance payable to a person to carry on the self-employed person's business is to be reduced by the value of the hours being worked by the self-employed person, as determined by the Board.
5. Housekeeping allowance(1) A person who suffers personal injury is entitled to a housekeeping allowance if at the time of the motor accident the person normally carried out household duties.(2) A housekeeping allowance is payable for either of the following periods during which the person is wholly disabled, by reason of the injury, from carrying out his or her normal household duties:(a) in relation to a person who has been an inpatient at a hospital for a continuous period of more than 4 days commencing on the day of the accident, any period within 39 weeks after the day of the accident;(b) in relation to any other person, any period within 26 weeks after the day of the accident.(3) A housekeeping allowance is payable at the lesser of the following rates:(a) a rate equivalent to the reasonable commercial cost of engaging a person to carry out the injured person's normal household duties;(b) $250 per week.(4) A housekeeping allowance is payable only in respect of those household duties that the injured person normally carried out at least once a week immediately before the accident.(5) If an injured person who is entitled to a housekeeping allowance under this clause –the injured person is entitled to recover only the cost of those duties that are additional to those carried out by the housekeeper before that date.(a) employed another person (the housekeeper) to carry out household duties before the date on which the person was injured; and(b) after the date on which the person was injured, required additional duties of the type referred to in subclause (4) to be carried out by the housekeeper or another person –
6. General limitations on disability allowances(1) A disability allowance is not payable for –(a) the period of 7 days beginning on the day of the motor accident; or(b) any period while the injured person is outside the Commonwealth.(2) A disability allowance is not payable unless, within the period of 20 days beginning on the day of the motor accident, the injured person –(a) in the case of an employed person's allowance or a self-employed person's replacement allowance, is wholly disabled, as a result of the injury, from engaging in his or her usual employment or occupation; or(b) in the case of a housekeeping allowance, is wholly disabled, as a result of the injury, from carrying out ordinary household duties.
7. Determination of average weekly earnings(1) In relation to the payment of a disability allowance, an injured person's average weekly earnings are to be determined by the Board as follows:(a) if the person was continuously engaged in employment or an occupation for the entire 12-month period immediately preceding the day of the motor accident, the person's average weekly earnings over that period;(b) if the person was continuously engaged in employment or an occupation immediately preceding the day of the motor accident for a period of one week or more and less than 12 months, the person's average weekly earnings over that period;(c) if the person was engaged in employment or an occupation immediately preceding the day of the motor accident for a period of less than one week, the average weekly earnings of a person engaged in the same, or as close as possible to the same, employment or occupation;(d) if the person was travelling to the place at which he or she was to take up his or her employment or occupation for the first time, the average weekly earnings of a person employed in the same, or as close as possible to the same, employment or occupation;(e) if the person was entitled to an employed person's allowance under clause 3(2)(c) of this Part, the person's average weekly earnings for those weeks in respect of which the person derived earnings in the 12 months immediately preceding the day of the motor accident.(2) For the purposes of this clause, the earnings of a person in respect of any period are to be determined by the Board as follows:(a) the remuneration he or she receives in any employment during that period;(b) the profits he or she receives in respect of the carrying on by him or her, either alone or in conjunction with any other person, of any business or undertaking during that period.
PART 6 - Disability benefits
1. Prostheses and other appliances(1) If a person suffers personal injury resulting directly from a motor accident, such expenses as are reasonably incurred by, or on behalf of, that person, for provision of such of the following as are reasonably required to alleviate the effect of the personal injury, are payable as disability benefits:(a) artificial limbs or other prostheses;(b) medical or surgical aids or appliances;(c) subject to subclause (2) , any other aid, appliance or equipment of a domestic nature determined by the Board to be appropriate in the circumstances.(2) Expenses incurred under subclause (1)(c) are not payable unless the Board has provided approval in writing before the aid, appliance or equipment is purchased.
2. Alterations to buildings and vehicles(1) Subject to subclause (2) , if a person suffers personal injury resulting directly from a motor accident, such expenses as are reasonably incurred by, or on behalf of, that person, in respect of such alterations to the following as are reasonably required to alleviate the effect of the injury, are payable as disability benefits:(a) the person's motor vehicle;(b) the building in which the person resides or proposes to reside.(2) Expenses under subclause (1) are not payable –(a) unless the Board has provided approval in writing before alterations to the vehicle or building are undertaken; and(b) in respect of alterations made more often than –(i) once every 5 years, in the case of a motor vehicle; or(ii) once every 15 years, in the case of a building.
3. Attendant careIf a person suffers personal injury resulting directly from a motor accident, such expenses as are reasonably incurred by, or on behalf of, that person, for the provision of attendant care reasonably required by the person as a result of having suffered the injury, are payable as disability benefits.
4. Domestic services for person requiring daily careIf a person suffers personal injury resulting directly from a motor accident and requires daily care in respect of that injury, such expenses as are reasonably incurred by, or on behalf of, that person, for the provision of domestic services reasonably required by the person as a result of having suffered the injury, are payable as disability benefits.
5. Gratuitous services to persons requiring daily care(1) If a person, who requires daily care in respect of personal injury resulting directly from a motor accident, requires attendant care or domestic services in respect of that injury, and the attendant care or domestic services are provided gratuitously, disability benefits are payable in respect of the attendant care or domestic services.(2) The amount of the disability benefits payable under subclause (1) is to be calculated by reference to the reasonable value of providing the attendant care or domestic services in the circumstances in which they are provided.
6. Limitation on disability benefits(1) If a person requires daily care in respect of personal injury resulting directly from a motor accident, the total daily, or weekly, expenses payable under clauses 3 and 4 of this Part and the total amount payable under clause 5 of this Part in respect of a person are not to exceed the total daily, or weekly, expenses that would be payable if the person was being provided with attendant care and domestic services in purpose-built group accommodation.(2) Disability benefits under this Part are only payable in respect of the following:(a) expenses incurred within the Commonwealth;(b) attendant care or domestic services provided within the Commonwealth.
7. Meaning of unreasonably incurred, &c.For the purposes of this Part –(a) an expense for an item is taken to have been unreasonably incurred to the extent that it exceeds the expense that would have been incurred if the item had been provided in the most economical manner practicable in the circumstances; and(b) the value of attendant care and domestic services provided gratuitously is taken to be unreasonable to the extent that the value exceeds the cost that would have been incurred if care and services had not been provided gratuitously but had been provided in the most economical manner practicable.
PART 7 - Counselling Services Benefits
1. Counselling services benefits(1) If –the expenses reasonably incurred by, or on behalf of, that family member for those counselling services are payable as counselling services benefits.(a) a person suffers personal injury resulting directly from a motor accident that occurs on or after 1 December 2007 and requires daily care, or has died, as a result of the personal injury; and(b) because of that injury or death, a family member of that person requires counselling services –(2) The maximum amount payable under subclause (1) of this Part in respect of a motor accident is –(a) if the accident occurred before 17 February 2020, $1 000 for each family member; or(b) [Part 7 of Schedule 1 Amended by No. 17 of 1996, Applied:17 Feb 2020] if the accident occurred on or after 17 February 2020, $1 270 for each family member.(3) For the avoidance of doubt, a benefit paid under Part 7 of Schedule 1 to the Motor Accidents (Liabilities and Compensation) Regulations 2010 in respect of a motor accident is taken to be a benefit paid under this clause in respect of that accident.
Displayed and numbered in accordance with the Rules Publication Act 1953.
Notified in the Gazette on 5 February 2020
These regulations are administered in the Department of State Growth.