Justices Rules 2003
The Magistrates Rule Committee, in the exercise of its powers under section 15AE of the Magistrates Court Act 1987 , makes the following rules of court for courts of summary jurisdiction exercising jurisdiction under the Justices Act 1959 .
PART 1 - Preliminary
These rules of court may be cited as the Justices Rules 2003 .
These rules of court take effect on 1 January 2004.
(1) In these rules of court –Act means the Justices Act 1959 ;Australia Post has the same meaning as in the Australian Postal Corporation Act 1989 of the Commonwealth;clerk means the clerk of petty sessions appointed under section 16A of the Act;Crown Law Officer has the same meaning as in section 1 of the Criminal Code ;first appearance means the first listing of a complaint where the defendant is required to respond to the complaint;forfeit means a forfeit under section 97 of the Local Government (Highways) Act 1982 ;public office has the same meaning as in the Local Government Act 1993 ;return day, in relation to a summons, means –(a) the day on which a response to the summons must be lodged or filed; or(b) the date on which the complaint is next listed before the court.(2) Unless the contrary intention appears, an expression defined in the Act has the same meaning in these rules of court.
(1) In these rules of court, a reference to a form by number is a reference to the form of that number in Schedule 1 .(2) A form set out in Schedule 1 –(a) is to be on A4 paper that is 297 millimetres in length by 210 millimetres in width; and(b) may be varied as circumstances require.
5. Procedure for matter not provided for
In any matter not otherwise provided for by these rules of court, the practice of the Supreme Court is to be followed.
PART 2 - Complaint and summons
Division 1 - Complaint
6. Form and making of complaint
(1) A complaint is to be in accordance with Form 1.(2) A complaint must be sworn before a justice.(3) [Rule 6 Subrule (3) substituted by S.R. 2009, No. 77, Applied:08 Jul 2009] Despite subrule (2) , a complaint made by a public officer does not need to be sworn before a justice.
7. Complaint to include reference to law contravened
A complaint must include a specific reference to the provision of the Act, regulation, by-law or other law that is alleged to have been contravened.
8. Description of property in complaint
(1) A description of property in a complaint must clearly identify the property in ordinary language.(2) If the offence to which the complaint relates does not require special ownership, a description of property in a complaint does not need to include the name of the owner of the property.
9. Description of ownership in complaint
If property is vested in more than one person and the owners of the property are referred to in a complaint, it is sufficient –(a) to describe the property as owned by one named person and another or others; or(b) to use a collective name without naming an individual if the owners of the property have a collective name.
10. Description of place, time, matter, act or omission in complaint
(1) A place, time, matter, act or omission mentioned in a complaint must be described with reasonable clarity.(2) If a time or place cannot be stated precisely in a complaint, it is sufficient to state the time or place as nearly as practicable.
11. Description of money in complaint
A description of money in a complaint does not need to include the form of the money.
12. Description of people in complaint
(1) A description and designation of the defendant or any other person in a complaint must be sufficient to identify the defendant or other person but does not necessarily have to state his or her correct name, address or occupation.(2) Despite subrule (1) , if in a complaint it is impracticable to give a description or designation that sufficiently identifies a person who is not the defendant as required by that subrule, it is sufficient –(a) to give a description or designation that is reasonably practicable; or(b) to describe that person as a person unknown.
13. Description of document, &., in complaint
The description of a seal, die, document or instrument in a complaint –(a) must describe the seal, die, document or instrument by the name or designation by which it is usually known, or by its subject matter; and(b) is not to include a copy of the seal, die, document or instrument.
14. Statement of intent in complaint
If an intent to defraud, deceive or injure is stated in a complaint, it is not necessary to state an intention to defraud, deceive or injure a particular person unless it is an essential ingredient of the offence.
(1) A complaint on oath is to be in accordance with Form 2.(2) A person making a complaint on oath must swear that the contents are true to the best of his or her knowledge and belief.(3) A complaint used as the basis of a warrant must be on oath.(4) On receipt of a complaint not made on oath, a justice may require it to be sworn on oath unless an Act provides otherwise.
A complaint, or a complaint and summons, containing lengthy particulars or other components may be set out on 2 or more sheets of paper which are securely fixed together at the top left-hand corner.
(1) The complainant –(a) may lodge the complaint with a clerk; and(b) must lodge the complaint within 7 days after the complaint is made.(2) If a summons is to be issued on a complaint, the complainant is to provide 3 copies of the complaint and the summons, with one copy to be filed with the clerk, another copy to be served under rule 20 and the remaining copy to be endorsed under rule 21 .
18. Complaint for breach of duty
A complaint of a breach of duty must –(a) set out the material facts on which the right to an order arises; and(b) end with an indication of the order being sought.
Division 2 - Summons
A summons is to be in accordance with Form 3 or Form 4.
(1) A summons may be served on a person other than a corporation by –(a) giving it to the person; or(b) leaving it for the person at his or her last-known, or usual, residential address with another person apparently living at that address who has attained the age of 16 years; or(c) leaving it for the person at his or her last-known, or usual, place of employment or business with another person apparently employed at that business who has attained the age of 16 years; or(d) posting it by registered mail to his or her last-known, or usual, residential or postal address, or address of business or employment.(2) A summons may be served on a corporation by –(a) delivering it to a director, the secretary, the public officer or another responsible officer of the corporation; or(b) posting it by registered mail to the registered office or place of business of the corporation.
A person serving a summons is to –[Rule 22 Rescinded by S.R. 2005, No. 38, Applied:18 May 2005] . . . . . . . .(a) endorse on a copy of the summons the date, place and mode of service in accordance with Form 5; and(b) sign the endorsement on the summons.
After a summons is endorsed under rule 21 , copies of the complaint and summons are to be –(a) lodged in the office of the clerk for the district in which the summons is returnable; and(b) filed by that clerk.
(1) Before or after the return day of a summons, a justice may extend the return day.(2) If the return day for a summons has been extended under subrule (1) , the justice who made the extension is to do the following on both the summons and a copy of the summons:(a) alter the date on which the summons is returnable;(b) place his or her initials and the date in the margin next to the alteration.
(1) An alteration to a summons at the time of its issue is to be initialled by the justice who issues the summons.(2) A failure to comply with subrule (1) does not invalidate the summons.
26. Notice taken to be summons
A notice issued under these rules of court, including a notice following an adjournment, requiring a defendant to appear at a specified time and place –(a) is taken to be a summons; and(b) may include a warning to the defendant that, if he or she does not appear when required by the notice, a warrant may be issued for his or her arrest; and(c) is to be served in the same manner as a summons unless otherwise provided in these rules.
PART 3 - Pleas
A defendant who is charged with an offence specified in Schedule 2 may plead in writing in the manner specified in rule 28 or 29 instead of appearing in person as required by the summons.
(1) A defendant may plead guilty under rule 27 and so be excused from attending court as required by the summons by –(a) signing the endorsement on the summons that is headed "PLEA OF GUILTY" in the presence of a justice who attests the defendant's signature; and(b) lodging the endorsed summons at the office of the clerk not less than 5 days before the time fixed for the hearing.(2) On receipt of a summons endorsed with a plea of guilty and attested as provided in subrule (1) , the justices may proceed as if the defendant had appeared and pleaded guilty to the complaint.(3) Despite subrule (1) , if the justices believe that the circumstances of a case warrant it, they may require the appearance of the defendant by issuing a notice to him or her under rule 32 .
29. Written plea of not guilty
(1) A defendant may plead not guilty under rule 27 and so be excused from attending court as required by the summons by –(a) signing the endorsement on the summons that is headed "PLEA OF NOT GUILTY" in the presence of a justice who attests the defendant's signature; and(b) lodging the endorsed summons at the office of the clerk not less than 5 days before the time fixed for the hearing.(2) On receipt of a summons endorsed with a plea of not guilty and attested as provided in subrule (1) , the clerk is to cause notice of a new hearing date to be served on the defendant in accordance with these rules.
30. First appearance of defendant not entitled to written plea
The first appearance of a defendant who is not entitled under rule 27 to plead in writing, or who has not pleaded in writing, is to take place at the time and place appointed in the summons.
31. Hearing in defendant's absence
(1) The justices may proceed to hear the case in the absence of a defendant if –(a) the defendant does not appear and the justices are satisfied that the defendant has been served with the summons or notice; or(b) the defendant does not answer to bail.(2) The justices may hear a case in accordance with subrule (1) whether or not the procedure under rule 32 has been applied.(3) In hearing a case in the absence of the defendant, the justices may receive the evidence they think fit either orally or by way of affidavit.
32. Non-appearance of defendant
If a defendant who has not pleaded in writing fails to appear at the time and place appointed in the summons or at an adjourned hearing, the justices may issue –(a) a notice requiring the defendant's appearance at a time and place specified in the notice; or(b) a warrant for the defendant's arrest.
PART 4 - Simple Offences
This Part applies in respect of a simple offence.
(1) If a defendant appears at the time and place appointed in a summons or by virtue of a warrant for his or her arrest and the complainant does not appear, the justices may –(a) dismiss the complaint; or(b) adjourn the proceedings and proceed in accordance with section 74B of the Act.(2) If a defendant does not appear at the time and place appointed in the summons, rules 31 and 32 apply.(3) If neither party appears at the time and place appointed in the summons, the justices may dismiss the complaint or adjourn the proceedings.
(1) If the defendant pleads not guilty or shows cause, the hearing is to proceed as follows:(a) before adducing evidence, the complainant may, or must if the justices so require, open the complainant's case;(b) if the complainant opens his or her case, the defendant, immediately after that opening and before evidence is adduced, may inform the justices of the issues expected to arise for determination by the justices;(c) before adducing evidence, the defendant may, or must if the justices so require, open the defendant's case;(d) after hearing any addresses made by the parties for the purpose of opening their case and after hearing the evidence, the justices are to –(i) convict the defendant; or(ii) dismiss the complaint; or(iii) make any other order as may be authorised by law;(e) at the close of evidence for the complainant, the defendant may submit that there is no case to answer and is not required to first elect whether he or she will call evidence;(f) neither party is entitled to address the justices at the conclusion of the evidence without the leave of the justices.(2) If the justices under subrule (1)(f) grant leave to a party to address them, the following apply:(a) the other party must be granted leave to address the justices also;(b) if the defendant has given evidence or adduced evidence, the defendant is to be given the opportunity to address the justices first;(c) if the defendant has not given evidence or adduced evidence, the complainant is to be given the opportunity to address the justices first.(3) If the defendant pleads guilty or, being present, does not show cause, the justices may convict the defendant or make any other order as may be authorised by law without hearing evidence.(4) Before imposing a penalty in respect of a conviction or order made under this rule, the justices may receive any evidence or statements as they think fit in order to inform themselves as to the circumstances of the case, the penalty to be imposed or the order to be made.
If a hearing of a simple offence is adjourned under section 74B of the Act without a certain time and place being appointed for the further hearing, the clerk –(a) may appoint a certain time and place; and(b) is to give notice in writing of that appointed time and place to the parties, or their legal representatives, if either party so requires.
A justice may order a defendant who is remanded in custody to be brought before him or her during the remand period and the person who has custody of the defendant must comply with the order.
38. Re-opening of hearing in defendant's absence
(1) On an application under subrule (2) , any 2 justices jointly may set aside any one or more of the following:(a) the dismissal of a complaint;(b) a conviction for the simple offence set out in the complaint that was recorded in the absence of the defendant;(c) an order arising from the hearing of a complaint made in the absence of the defendant.(2) An application to have a dismissal, conviction or order set aside by justices under subrule (1) must be –(a) made in writing by the person –(i) whose complaint was dismissed; or(ii) against whom, or in the absence of whom, the conviction or order was made; and(b) lodged with the clerk of the court where the complaint was dismissed or where the conviction or order was made; and(c) supported by oral evidence or affidavit; and(d) accompanied by proof of service on the other party of notice of the application to set aside.(3) For the purposes of subrule (1) , a dismissal, conviction or order may be set aside on the terms, as to costs or otherwise, that the justices think fit.(4) Despite any other provision of this rule, a conviction or order made in the absence of the defendant may be set aside without the appearance of either party if the consent of both parties is endorsed on the application.(5) After setting aside the dismissal, conviction or order, the justices may –(a) proceed to hear and determine the complaint that was dismissed or the complaint in relation to which the conviction or order was made; or(b) direct that –(i) the complaint be reheard and determined at the time and place they specify; and(ii) any notice they specify is to be given to any person they think necessary.
39. Execution of conviction or order
(1) As soon as practicable after the making of a conviction or order that –the clerk is to deliver personally or by post to the defendant a written notice informing him or her of the making and details of the conviction or order, including details of any disqualification or disability imposed.(a) is made in relation to a simple offence; and(b) is made in the absence of the defendant; and(c) does not involve imprisonment –(2) If a conviction or order referred to in subrule (1) requires the defendant to pay an amount, the notice under that subrule is to include –(a) details of that amount; and(b) the date on or before which payment is required to be made; and(c) the time and place at which payment may be made; and(d) particulars of the instalments to be paid if the justices have ordered payment to be made in instalments.(3) A person required under a conviction or order to pay an amount of money is to pay that amount, or any instalment of that amount, as the clerk directs, unless the justices otherwise direct.(4) If a person who is required under a conviction or order to pay an amount of money pays that amount to a person other than the clerk, the person receiving that amount is to –(a) account to the clerk for that amount; and(b) if required by the clerk, pay that amount to the clerk.(5) Subrule (4) does not apply if the court has directed payment of the amount of money to the person who receives the money.(6) A warrant of execution is to order the person to whom it is directed to pay the amount of money and costs to be levied as the clerk directs.(7) If a person who is required under a warrant of execution to pay an amount of money pays that amount to a person other than the clerk, the person receiving that amount is to pay it to the clerk as soon as practicable.
PART 5 - Breach of Duty
40. Application of Part 4 to complaint for breach of duty
Except as otherwise provided, Part 4 applies to a complaint for a breach of duty with all necessary modifications and as if "conviction" includes "order".
PART 6 - Parking Meters
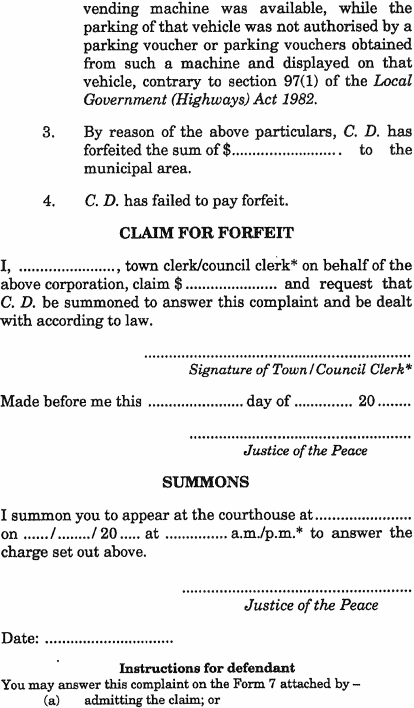
(1) A complaint and summons for a forfeit is to be made in accordance with Form 6.(2) Two copies of Form 7 must be attached to a summons at the time it is served.(3) The return day for a summons is to be at least 21 days after the complaint for a forfeit is made.(4) If it is likely that there will be less than 14 days between the day on which the defendant receives the summons and the return day, the complainant must apply for an extension of the summons under rule 24 .(5) Except as otherwise provided by this Part, Part 2 applies to a complaint and summons for a forfeit.
On receipt of a summons for a forfeit, the defendant may plead to the complaint for the forfeit by –(a) completing a copy of Form 7 that was attached to the summons under rule 41(2) ; and(b) lodging the completed Form 7 at a public office within 7 days after being served with the summons.
(1) If a defendant pleads to the complaint for a forfeit under rule 42 , he or she is not bound to attend court as required by the summons.(2) If the complainant appears at court at the time the defendant was required to appear but the defendant is not bound to attend court, the complainant is to bring and produce to the court the Form 7 lodged at the public office by the defendant under rule 42(b) .(3) If the defendant is not bound to attend court and the defendant has notified the complainant on the defendant's Form 7 that the defendant intends to appear at the hearing, the complainant may avoid further liability in the matter by giving the defendant and the clerk 2 clear days' notice in writing that he or she withdraws the complaint.
(1) Rule 35(3) does not apply to the hearing of a complaint for a forfeit.(2) If, at a hearing of a complaint for a forfeit –the justices are to proceed to hear evidence and legal argument on the issues appearing on the complaint for the forfeit and Form 7.(a) the defendant has pleaded in accordance with rule 42 ; and(b) the complainant appears; and(c) the complainant produces the Form 7 lodged at the public office by the defendant under rule 42(b) –(3) Before proceeding under subrule (1) to hear evidence and legal argument on the issues appearing on the complaint for the forfeit and the Form 7, the justices may grant leave for the complaint or Form 7, or both, to be amended.(4) If, at a hearing of a complaint for a forfeit, the defendant and complainant both appear and the defendant has not pleaded under rule 42 , the justices are to –(a) state to the defendant the substance of the complaint; and(b) ask the defendant how he or she pleads; and(c) proceed to hear the evidence and legal argument of the issues appearing on the complaint for a forfeit.(5) If, at a hearing of a complaint for a forfeit, the defendant does not appear and has not pleaded under rule 42 but the complainant does appear, the justices are to determine the amount of the forfeit as if they were imposing a penalty.
(1) In this rule –delaying plea means a plea showing that, even if the complaint were true, the justices have no jurisdiction to hear the complaint and the complaint should not proceed;plea of general bar means a plea that the defendant owes nothing.(2) The defendant may answer a complaint for a forfeit by –(a) demurring; or(b) pleading –(i) a delaying plea; or(ii) a plea of general bar; or(iii) a bar to proceedings under section 100(3) of the Local Government (Highways) Act 1982 ; or(c) demurring and pleading together.(3) If possible, a delaying plea must show when the complaint can proceed.(4) A plea of general bar –(a) may give facts that are not the subject of a delaying plea or a bar to proceedings under section 100(3) of the Local Government (Highways) Act 1982 ; and(b) is to give particulars that exclude irrelevant evidence and enable the complainant to know what case he or she has to meet.
PART 7 - Indictable offences
This Part applies in respect of indictable offences.
A justice may order a defendant who is remanded in custody to be brought before the justice before the remand period expires and the person with custody of the defendant must comply with the order.
48. Form of words for election by defendant
For the purposes of section 72(1) of the Act, the following words are prescribed:
The offence with which you are charged is indictable, which means that it is normally treated as a criminal charge and is heard in the Supreme Court.
In some cases the law says the case may be disposed of in the lower court.
This is one of those cases, and the choice is yours as to which court hears it.
Are you willing to be tried here or do you wish to be tried in the Supreme Court by a jury?
49. Transmission of deposition
(1) If a defendant is committed for trial or for sentence, the clerk, without delay, is to –(a) transmit to the Director of Public Prosecutions the following documents:(i) the complaint with the committal order enclosed;(ii) any depositions taken under the Act;(iii) all recognisances taken in the matter;(iv) a list of the witnesses who have been bound over to attend the trial conditionally;(v) the documents and articles produced in evidence and retained by the justice;(vi) a list of the exhibits produced in evidence;(vii) a minute of the order certified by the clerk; and(b) transmit to the Registrar of the Supreme Court a certified copy of the following documents:(i) the complaint with committal order enclosed;(ii) any order relating to bail;(iii) any recognisances taken in the matter.(2) The defendant is entitled to receive copies of the complaint, depositions and the order of committal or discharge –(a) from the person who has custody of those documents; and(b) at any time after all the depositions have been taken.
PART 8 - Suspended Sentences
50. Breach of suspended sentence
A person intending to make a complaint, or file an application, about a breach of a condition of a suspended sentence must file the complaint or application with the clerk of the court that imposed the suspended sentence.
PART 9 - Warrants
51. Warrant noted on complaint
If a warrant of apprehension is issued on a complaint, the justice issuing the warrant is to make a note of the warrant on the complaint and send the complaint to the clerk as soon as practicable.
(1) A warrant to apprehend a defendant so that he or she may answer a complaint may be directed to –(a) a police officer by name; or(b) all police officers without naming them; or(c) to a named police officer and all other police officers.(2) If a police officer named in a warrant is unable to act on the warrant, another police officer may execute the warrant.
A warrant –(a) remains in force until executed; and(b) may be executed anywhere within the State.
Warrants of apprehension and search warrants may be granted, issued and executed on –(a) a Sunday as on any other day; and(b) a statutory holiday under the Statutory Holidays Act 2000 as on any other day.
PART 9A - Victim Impact Statements
[Rule 54A Inserted by S.R. 2004, No. 177, Applied:29 Dec 2004] In this Part –[Rule 54A Amended by S.R. 2006, No. 138, Applied:20 Dec 2006] Court means a court of petty sessions;[Rule 54A Amended by S.R. 2006, No. 138, Applied:20 Dec 2006] [Rule 54A Amended by S.R. 2014, No. 45, Applied:16 Apr 2014][Rule 54A Amended by S.R. 2014, No. 45, Applied:16 Apr 2014] victim means –(a) a victim within the meaning of section 81A of the Sentencing Act 1997 or section 36A of the Youth Justice Act 1997 ; or(b) a person allowed to furnish to the Court a written statement under section 81A(2A) of the Sentencing Act 1997 or section 36A(3) of the Youth Justice Act 1997 ;[Rule 54A Amended by S.R. 2014, No. 45, Applied:16 Apr 2014] victim impact statement means a statement furnished under section 81A of the Sentencing Act 1997 , or section 36A of the Youth Justice Act 1997 , by a victim of an offence.
54B. Duty of victim to provide copies of victim impact statement
[Rule 54B Inserted by S.R. 2004, No. 177, Applied:29 Dec 2004](1) A victim who wishes to furnish to the Court a victim impact statement is to provide the original of the statement to the prosecutor, and the prosecutor is to provide a copy of the statement to –(a) the offender; or(b) if the offender is represented, his or her counsel.(2) On providing the statement under subrule (1), the victim is to advise the prosecutor whether he or she wishes to read the statement to the Court.
54C. Provision of victim impact statement to Court
[Rule 54C Inserted by S.R. 2004, No. 177, Applied:29 Dec 2004] The prosecutor is to –(a) provide to the Court any victim impact statement relating to an offence which has been provided by a victim of the offence; and(b) inform the Court whether the victim has requested to read the statement to the Court.
54D. Reading of victim impact statement
[Rule 54D Inserted by S.R. 2004, No. 177, Applied:29 Dec 2004] [Rule 54D Substituted by S.R. 2006, No. 138, Applied:20 Dec 2006] A victim impact statement is to be read to, or by, the Court before the Court passes sentence on the offender.
54E. Postponement of reading of victim impact statement
[Rule 54E Inserted by S.R. 2004, No. 177, Applied:29 Dec 2004] If a victim has requested to read a victim impact statement to the Court but is not present in Court, the Court may postpone the reading of the statement and is to cause notice of the time fixed for the reading of the statement to be given to the victim.
54F. Power of victim to amend victim impact statement
[Rule 54F Amended by S.R. 2006, No. 138, Applied:20 Dec 2006] [Rule 54F Inserted by S.R. 2004, No. 177, Applied:29 Dec 2004] Subject to rule 54G, a victim who has furnished a victim impact statement may amend the statement at any time before it is read to, or by, the Court.
54G. Power of Court to exclude irrelevant material
[Rule 54G Inserted by S.R. 2004, No. 177, Applied:29 Dec 2004] If the Court so directs, a victim is not to read out to the Court any part of the victim impact statement that the Court considers to be irrelevant to the proceedings.
54H. Power of victim to withdraw victim impact statement
[Rule 54H Amended by S.R. 2006, No. 138, Applied:20 Dec 2006] [Rule 54H Inserted by S.R. 2004, No. 177, Applied:29 Dec 2004] A victim who has provided a victim impact statement may withdraw the statement at any time before it is read to, or by, the Court and, if he or she does so, the statement is not to be read to, or by, the Court.
54I. Requirements for victim impact statement
[Rule 54I Inserted by S.R. 2004, No. 177, Applied:29 Dec 2004] A victim may furnish to the Court only one victim impact statement and the statement –(a) is to be legible; and(b) is to be in the English language; and(c) may be either printed or handwritten; and(d) except with the leave of the Court, may not be longer than 20 pages, inclusive of medical reports and other annexures; and(e) may, but need not, be in a form approved by the Chief Magistrate.
PART 9B - Practice and procedures under Family Violence Act 2004
Division 1 - Interpretation[Division 1 Inserted by S.R. 2005, No. 18, Applied:30 Mar 2005]
(1) In this Part –application means an application for an order made under Part 3 or Part 4 of the Family Violence Act 2004 ;EFVO means an external family violence order within the meaning of the Family Violence Act 2004 ;electronic copy means a copy of a document made by facsimile or electronic transmission;endorsed copy means –(a) a copy of an order or application, which contains an endorsement of service; or(b) a facsimile copy of the copy referred to in paragraph (a) ;order means an order made under Part 3 or Part 4 of the Family Violence Act 2004 and includes any conditions contained in the order.(2) Unless the contrary intention appears, an expression used in this Part has the same meaning as it has in Part 1 of the Family Violence Act 2004 .
Division 2 - Applications[Division 2 Inserted by S.R. 2005, No. 18, Applied:30 Mar 2005]
(1) This Division applies to an application for –(a) an FVO; and(b) a variation to, or extension or revocation of, an FVO or PFVO.(2) This Division does not apply to an application for the registration of an EFVO, unless otherwise specified.
An application is to –(a) specify the order sought; and(b) [Rule 54L Amended by S.R. 2005, No. 90, Applied:10 Aug 2005] include –(i) in the case of an application made by a police officer, a statutory declaration of the officer that to the best of his or her knowledge and belief the information contained in the application is true; or(ii) in the case of any other applicant, an affidavit of the person that to the best of his or her knowledge and belief the information contained in the application is true; and(c) be filed with the clerk.
54M. Electronic filing of applications
Where an application is filed by a person, firm, corporation or government agency approved under rule 65(2) , the person, firm, corporation or agency is to retain the original sworn application and produce it to a magistrate on request.
(1) A person making an application is to, as soon as practicable after it is filed with the clerk, cause a sealed copy of the application to be served personally on –(a) in the case of an application for an FVO or an application for a variation to, or extension or revocation of, an FVO, on all other parties to the application; or(b) in the case of an application for a variation to, or extension or revocation of, a PFVO, on all other parties to the application and on the Commissioner of Police.(2) Where a police officer is the applicant for the revocation of an FVO or a PFVO, service of a sealed copy of the application is not required.(3) A person who serves a sealed copy of an application is to –(a) endorse a copy of the application with a memorandum stating the day, place and mode of service; and(b) sign the memorandum; and(c) as soon as practicable, cause the endorsed copy to be lodged with the clerk for the district in which it is returnable.
A respondent to an application who wishes to oppose the application must –(a) as soon as practicable and before the return date of the application, file with the clerk an affidavit setting out the grounds of his or her opposition; and(b) cause the affidavit to be served personally on all the other parties to the application as soon as practicable after filing it; and(c) after it has been served –(i) endorse a copy of the application with a memorandum stating the day, place and mode of service; and(ii) cause the person who served the affidavit to sign the memorandum; and(iii) as soon as practicable, cause the endorsed copy to be lodged with the clerk for the district in which it is returnable.
(1) At the hearing of an application under this Part, evidence may be given by affidavit.(2) A person who makes an affidavit for the purposes of subrule (1) is not required to attend the hearing of the application unless a party to the proceedings, or the justice, so requires.(3) By notice in writing given to the person who made an affidavit for the purposes of subrule (1) , a party to the proceedings may require that the person attend the hearing for cross-examination and, if the person fails to attend, the court may –(a) refuse to allow the affidavit to be used; or(b) allow the affidavit to be used on any conditions the court thinks fit; or(c) adjourn the proceedings until the person attends for cross-examination.(4) Notice under subrule (3) is to be given not less than 10 clear working days before the proceedings.
Division 3 - Miscellaneous[Division 3 Inserted by S.R. 2005, No. 18, Applied:30 Mar 2005]
(1) If an FVO or interim FVO is made, varied or extended a copy of the order as made, varied or extended is to be served personally on the respondent as soon as practicable after it is made, varied or extended.(2) [Rule 54Q Subrule (2) substituted by S.R. 2005, No. 38, Applied:18 May 2005] If an FVO or interim FVO is made, varied or extended by a magistrate while the respondent is present in court, the magistrate may order that the FVO or interim FVO be served on any person and in any manner the magistrate thinks fit.(3) If an FVO or interim FVO is made, the clerk must forward a copy of the order –(a) to the Commissioner of Police; and(b) to the person who made the application for the order; and(c) if the person who made the application is not the person for whose benefit the order is made –(i) to the person for whose benefit the order is made; or(ii) if the person referred to in subparagraph (i) is a child, to his or her legal guardian.(4) If an FVO or interim FVO is varied or extended, the clerk, as soon as practicable after the order is varied or extended, is to forward a copy of the order as varied or extended –(a) to the Commissioner of Police; and(b) to the person who made the application for the variation to or extension of the order; and(c) if the person who made the application is not the person for whose benefit the order is made –(i) to the person for whose benefit the order is made; or(ii) if the person referred to in subparagraph (i) is a child, to his or her legal guardian.(5) If a registered EFVO is varied or extended, the clerk, as soon as practicable after the variation or extension is made, is to forward a copy of the order, as varied or extended, to –(a) the Commissioner of Police; and(b) the person who made the application for the variation or extension.(6) On the revocation of an FVO, an interim FVO or a registered EFVO, the clerk must notify the following persons of that revocation:(a) the Commissioner of Police;(b) all parties to the application for the order.(7) If a PFVO is varied, extended or revoked by the court, the clerk must notify the following persons of the variation, extension or revocation:(a) the Commissioner of Police;(b) all parties to the application for the order.(8) If an FVO, an interim FVO or a PFVO, including any such order as varied or extended, is served on the person against whom the order is made, the person who served the order is to –(a) endorse on the copy of the order a memorandum stating that the order has been served; and(b) sign the memorandum and specify the date on which the order was served; and(c) forward a copy of the endorsed copy to the clerk.(9) On receipt of the copy of the order endorsed in accordance with subrule (8)(a) , the clerk is to notify the fact that the order has been served and the date on which it was served to –(a) the applicant for the order or its variation or extension; and(b) the person for whose benefit the order was made if that person was not also the applicant; and(c) the Commissioner of Police.(10) Evidence of service of a sealed copy of an application under rule 54N may be provided by –(a) the sworn evidence of the person serving it; or(b) the endorsed copy.(11) An endorsement of service or an electronic copy of an endorsement of service is evidence, until the contrary is shown –(a) that the endorsement was signed by the person whose signature it purports to be; and(b) that the statements contained in the endorsement are true.
54R. Provisions in respect of children
(1) Where a child is an affected child or a party to an FVO or interim FVO, including a PFVO that is varied, extended or revoked by the court, the clerk is to notify the Secretary of the responsible Department in relation the Children, Young Persons and Their Families Act 1997 –(a) of the current status of the order; and(b) where applicable, when service of the order has been effected.(2) Notification for the purposes of subrule (1) may be by transmission of an electronic copy of the order.
54S. Power of justices to dispense with Part
Justices may, upon such terms and conditions as they think necessary, dispense with the need for a party to proceedings under Part 4 of the Family Violence Act 2004 to comply with any provision of this Part.
[Rule 54T Substituted by S.R. 2009, No. 77, Applied:08 Jul 2009] The court, when constituted by one or more justices (one of whom is not a magistrate), may exercise only the following jurisdiction under the Family Violence Act 2004 :(a) the granting or refusal of bail under section 12 of that Act;(b) the making, variation, extension or revocation of an interim FVO under section 23 of that Act;(c) the revocation (but not the making, variation or extension) of an FVO under section 20 of that Act.
PART 10 - Appeals
55. Form of notice of appeal to magistrate
A notice of appeal for the purposes of section 113A of the Act is to be in accordance with Form 8.
A summons for the purposes of section 113A(6) of the Act is to be in accordance with Form 9.
57. Form of application to magistrate to review
An application to review under section 113B of the Act is to be in accordance with Form 10.
(1) For the purposes of section 109(2) of the Act, the following documents are prescribed for transmission to the Registrar of the Supreme Court:(a) the complaint and any amendments;(b) the notes of evidence or a copy of the notes of evidence taken by the justices or the audio recording of proceedings, if recorded;(c) the reasons for judgment, if given in writing, or the audio recording, if recorded;(d) the list of exhibits;(e) any exhibits which are documents;(f) a copy of the record of the court's proceedings required to be taken under section 50A of the Act;(g) in the case of a notice to review a sentence –(i) the reasons for sentence, if given in writing, or the audio recording, if recorded; and(ii) copies of the record of conviction; and(iii) copies of other documents lodged with the court as part of the sentencing process, if any.(2) If a public officer is a party to a notice to review, the clerk is to forward a certified copy of the documents referred to in subrule (1) to the Director of Public Prosecutions.
59. Voluntary resumption of sentence
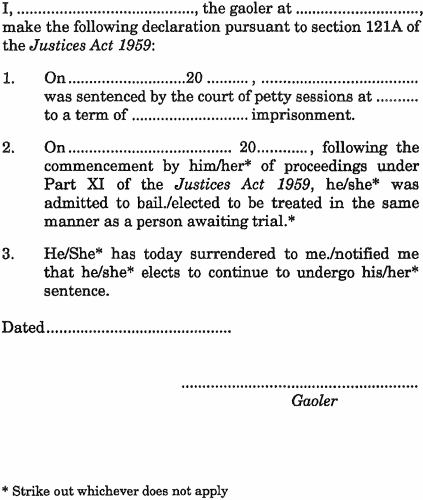
(1) A declaration by a gaoler for the purposes of section 121A(3) of the Act is to be –(a) in accordance with Form 11; and(b) retained in the prison records.(2) As soon as practicable after making the declaration, the gaoler is to forward a copy to the clerk of the court which imposed the sentence to which the declaration relates.
An appeal to a magistrate under section 125B of the Act is to be in accordance with Form 12.
61. Appeal to Supreme Court against order for bail
An appeal to the Supreme Court under section 125C of the Act is to be –(a) made by notice in writing; and(b) supported by an affidavit specifying the material facts on which the appellant wishes to rely, unless a judge otherwise orders.
PART 11 - Miscellaneous
62. Application of Part 4 to applications
Except as otherwise provided, Part 4 applies to an application with all necessary modifications and as if "complaint" includes application.
63. Re-opening of hearing of application in defendant's absence
(1) On an application under subrule (2) , any 2 justices jointly may set aside any one or more of the following matters:(a) the dismissal of an application;(b) an order arising from the hearing of an application made in the absence of the defendant or respondent.(2) An application to have a dismissal or order set aside by justices under subrule (1) must be –(a) made in writing by the person –(i) whose application was dismissed; or(ii) against whom, or in the absence of whom, the order was made; and(b) lodged with the clerk of the court where the application was dismissed or where the order was made; and(c) supported by oral evidence or affidavit; and(d) accompanied by proof of service on the other party of notice of the application to set aside.(3) For the purposes of subrule (1) , a dismissal or order may be set aside on the terms, as to costs or otherwise, that the justices think fit.(4) Despite any other provision of this rule, an order made in the absence of the defendant may be set aside without the appearance of either party if the consent of both parties is endorsed on the application.(5) After setting aside the dismissal or order, the justices may –(a) proceed to hear and determine the application that was dismissed or the application in relation to which the order was made; or(b) direct that –(i) the application be reheard and determined at the time and place they specify; and(ii) any notice they specify is to be given to any person they think necessary.
(1) The justices may adjourn proceedings to another court under section 50B(1) of the Act by announcing the adjournment in open court.(2) If one or both of the parties is absent during the announcement of an adjournment under subrule (1) , the clerk of the court is to inform that party, or those parties, by ordinary mail.(3) The absence of one or both of the parties does not affect the making of the adjournment of proceedings to another court.(4) Despite subrule (2) , the justices may determine that an absent party is not entitled to be informed of the adjournment.(5) The clerk is to forward all documents in his or her possession concerning the adjourned proceedings to the clerk of the court to which the proceedings are adjourned, together with –(a) a minute of the order under section 50B(1) of the Act; or(b) the original consent signed pursuant to section 50B(2) of the Act.(6) If the justices give written consent to an adjournment under section 50B(2) and the date of the adjournment is not specified in the consent, the clerk of the court receiving the proceedings is to advise both parties in the usual way of the date to which the proceedings are adjourned.(7) If proceedings are adjourned to another court, the original bail is to continue until the next hearing unless an order is made to the contrary.
65. Electronic documents and records of information
(1) The Chief Magistrate may approve one or more of the following:(a) the provision or exchange of documents required to be done under these rules by electronic exchange or provision of documents between computers;(b) the recording of administrative and judicial information required to be kept under these rules by electronic recording;(c) the recording of proceedings in court, or before a justice, by mechanical, electronic, digital or other means.(2) [Rule 65 Subrule (2) amended by S.R. 2005, No. 18, Applied:30 Mar 2005] The Chief Magistrate is to approve a person, firm, corporation or government agency who wishes to provide or exchange documents electronically or record information electronically under subrule (1) .(3) The Chief Magistrate, in writing, may revoke an approval under subrule (1) by lodging the revocation at each district registry.(4) The Chief Magistrate may revoke an approval under subrule (2) by giving written notice of the revocation to the person whose approval to provide or exchange documents electronically or record information electronically is revoked.
66. Period for which tape is to be preserved
Tapes, or other apparatus onto which proceedings or depositions are recorded by mechanical or electronic means, are to be preserved for the following periods:(a) in the case of a transcript of proceedings that relate to a complaint where a notice to review an order made by justices is filed in the Supreme Court, until the determination of the notice to review;(b) in the case of a transcript of proceedings that relate to a complaint where an appeal against an order made by a court of petty sessions (other than a court constituted by a magistrate) is made to a magistrate, until the determination of the appeal;(c) in the case of a transcript of a deposition relating to any cause or matter under the Act, until the determination of the matter in the Supreme Court;(d) in any other case, for a period of 3 months after the making of the recording.
67. Means by which a person appears before justices
(1) If a person is required to appear or be brought before the justices for any purpose, the person may appear or be brought before the justices –(a) in person; or(b) by audio visual link within the meaning of the Evidence (Audio and Audio Visual Links) Act 1999 ; or(c) if the justices direct, by any other means in accordance with that direction.(2) Despite subrule (1)(b) and (c) , the justices may direct that the person be brought before them in person.
68. Taking evidence and receiving submission
The justices may announce findings or orders, take evidence, receive submissions or sentence a person in relation to any proceedings by –(a) the personal appearance of a person; or(b) audio link or audio visual link, within the meaning of the Evidence (Audio and Audio Visual Links) Act 1999 ; or(c) any other means of communication.
68AA. Written statements or reports as evidence
[Rule 68AA Inserted by S.R. 2008, No. 121, Applied:08 Oct 2008](1) This rule does not apply to preliminary proceedings under section 61 of the Justices Act 1959 .(2) In any proceedings, the justices may, upon such terms and conditions as they think necessary, allow a written statement or report by a person to be tendered or treated as evidence in chief of that person.
[Rule 68A Inserted by S.R. 2005, No. 38, Applied:18 May 2005](1) Evidence of the service of an application, an affidavit, an order, a notice, a complaint, a summons or any other court process may be provided by –(a) a memorandum signed by the person who served it; or(b) the sworn evidence, affidavit or statutory declaration of that person.(2) A memorandum of service is to include details of the date, time, place and method of service and the full name and address of the person who served it.(3) A memorandum of service is evidence, until the contrary is shown –(a) that the memorandum was signed by the person whose signature it purports to be; and(b) that the statements contained in the memorandum are true.(4) If service of any court process was effected on a person by registered mail, service of the court process may be proved by –unless the person proves that the court process was not received by that person or another person on that person's behalf.(a) a signed memorandum on the court process referred to in subrule (1) that specifies the serial number of an apparently duly completed registered mail posting receipt of Australia Post for the registered mail by which the court process was served together with –(i) the apparently duly completed registered mail posting receipt of Australia Post bearing that serial number; and(ii) an apparently duly completed return card of Australia Post showing that a registered mail article, bearing the serial number referred to in subparagraph (i) , was received by –(A) in the case of any court process other than a summons, any person; or(B) in the case of a summons, a person referred to in rule 20(1) ; or(b) the sworn evidence of the person who served the court process together with the documents referred to in paragraph (a)(i) and (ii) –
68B. Evidence of receipt of notice to attend by police witness
[Rule 68B Inserted by S.R. 2007, No. 139, Applied:26 Dec 2007] If in a proceeding under the Act an issue arises as to whether a police officer has received notice, other than by way of a summons under section 41 of the Act, requiring him or her to attend as a witness in that proceeding, the justices may inquire into and inform themselves on that issue in such manner as they think fit, subject to the rules of natural justice.
If a procedure for an approach to the court of petty sessions is not otherwise provided by the Act, any other Act or these rules, the approach may be made by application in accordance with Form 13 modified as the circumstances require.
70. Formal record of conviction
It is not necessary to draw up a conviction, order or record of a decision, unless it –(a) is required by a party to the proceedings for the purposes of an appeal against the decision; or(b) is required for the purpose of a return to a writ of habeas corpus or an order to review under the Judicial Review Act 2000 from the Supreme Court.
(1) The clerk is to keep a record for each matter coming before the court.(2) The record is to contain a summary of the course of the proceedings on the complaint but not the evidence.(3) Without limiting the generality of subrule (2) , the summary is to include –(a) the date of the hearing (original and adjourned); and(b) the names of the presiding justices and persons appearing; and(c) the pleas; and(d) a record of adjournments; and(e) the names of witnesses examined; and(f) a detailed statement of the result, including convictions and orders.
72. Inspection of court record
(1) In respect of proceedings under these rules, the record of those proceedings is to be available for inspection without fee by –(a) a party to the proceedings; or(b) a Crown Law Officer.(2) The clerk may permit the record of proceedings held in open court, and the register entries in respect of those proceedings, to be inspected without payment of a fee by a person other than a party to those proceedings or a Crown Law Officer.
A summons or warrant is to be signed by the justice issuing it.
SCHEDULE 1 - Forms
Form 1 - Complaint
Form 2 - Complaint on Oath
Form 3 - Summons
Form 4 - Summons
Form 5 - Memorandum of Service
Form 6 - Complaint and Summons
Form 7 - Answer
Form 8 - Notice to Appeal
Form 9 - Summons
Form 10 - Application for Review
Form 11 - Declaration as to Resumption of Sentence
Form 12 - Notice of Appeal
Form 13 - Application
SCHEDULE 2 - OffencesFor the purpose of rule 27 , the following offences are specified offences:[Schedule 2 Amended by S.R. 2006, No. 138, Applied:20 Dec 2006] [Schedule 2 Amended by S.R. 2006, No. 138, Applied:20 Dec 2006] [Schedule 2 Amended by S.R. 2006, No. 138, Applied:20 Dec 2006] [Schedule 2 Amended by S.R. 2009, No. 150, Applied:02 Dec 2009] [Schedule 2 Amended by S.R. 2010, No. 111, Applied:24 Nov 2010] [Schedule 2 Amended by No. 60 of 2011, Sched. 1, Applied:01 Jul 2013] [Schedule 2 Amended by No. 60 of 2011, Sched. 1, Applied:01 Jul 2013] [Schedule 2 Amended by S.R. 2013, No. 68, Applied:04 Sep 2013] [Schedule 2 Amended by No. 50 of 2013, Sched. 1, Applied:11 Dec 2013] [Schedule 2 Amended by No. 14 of 2024, s. 23, Applied:01 Feb 2025]
1. | An offence under section 40 of the Ambulance Service Act 1982 | 2. | An offence under the Animal Welfare Act 1993 , and any regulations made under that Act, if the maximum penalty for the offence does not exceed 10 penalty units | 3. | An offence under section 5(4) or 9 of the Bail Act 1994 | 4. | An offence under the Classification (Publications, Films and Computer Games) Enforcement Act 1995 , except Part 8, and any regulations made under that Act | 5. | An offence under section 16 of the Consumer Affairs Act 1988 | 6. | An offence under the Dog Control Act 2000 | 7. | An offence under the Environmental Management and Pollution Control Act 1994 , and any regulations made under that Act, if the maximum penalty for the offence does not exceed 10 penalty units | 8. | An offence under the Forest Management Act 2013 and any regulations made under that Act | 8A. | An offence under the Heavy Vehicle National Law (Tasmania) Act 2013 , except sections 30(1), 228(1), 250(1), 251(1), 254(1), 256(1), 258(1), 260(1), 533(7) and 534(5) of the Heavy Vehicle National Law (Tasmania), and any regulations that apply in Tasmania for the purposes of that Law | 9. | An offence under the Inland Fisheries Act 1995 if the maximum penalty for the offence does not exceed 10 penalty units | 10. | An offence under the Inland Fisheries (Recreational Fishing) Regulations 2009 | 11. | An offence under the Liquor Licensing Act 1990 if the maximum penalty for the offence does not exceed 10 penalty units | 12. | An offence under the Litter Act 2007 | 13. | An offence under section 203 or 204 of the Living Marine Resources Management Act 1995 , and any regulations or rules made under that Act, if the maximum penalty for the offence does not exceed 10 penalty units | 14. | An offence under any by-laws under the Local Government Act 1993 , the University of Tasmania Act 1992 or the Local Government (Highways) Act 1982 | 15. | An offence under the Marine and Safety Authority Act 1997 , and any regulations or by-laws made under that Act, if the maximum penalty for the offence does not exceed 10 penalty units | 16. | An offence under section 29 of the Motor Accidents (Liabilities and Compensation) Act 1973 | 17. | An offence under the National Parks and Reserves Management Act 2002 | 18. | An offence under the National Parks and Reserved Land Regulations 2009 | 19. | An offence under the Passenger Transport Services Act 2011 and any regulations made under that Act | 20. | An offence under section 13 , 14 , 14B , 15(1) , 15A , 15B , 15C , 16 , 17 , 19A , 20AA , 25 , 34B , 37(1) , 37(3) , 37(4) , 41 , 43 , 55A or 57 of the Police Offences Act 1935 | 21. | An offence under the Public Health Act 1997 , and any regulations made under that Act, if the maximum penalty for the offence does not exceed 10 penalty units | 22. | An offence in regulations made under the Racing Regulation and Integrity Act 2024 if the maximum penalty for the offence does not exceed 10 penalty units | 23. | An offence under the Roads and Jetties Act 1935 | 24. | An offence under the Road Rules 2009 | 25. | An offence under section 7 of the Road Safety (Alcohol and Drugs) Act 1970 | 26. | An offence under the Taxi and Hire Vehicle Industries Act 2008 and any regulations made under that Act | 27. | An offence under section 41(1) or 51(3) of the Traffic Act 1925 | 28. | An offence under the Vehicle and Traffic Act 1999 , except sections 9 , 13 , 14 , 15 , 18 , 31 and 64 , and any regulations made under that Act | 29. | An offence under the Wellington Park Regulations 2009 | 30. | An offence under the Wildlife Regulations 1999 |
These rules of court were made by the Magistrates Rule Committee at a meeting held on 15 December 2003.
A. G. Shott
Chief Magistrate
M. R. Hill
Deputy Chief Magistrate
Z. Szramka
Member
P. H. Wilson
Member
S. E. Tennent
Member
P. F. Dixon
Member
S. F. Mollard
Member
I. R. Matterson
Member
Displayed and numbered in accordance with the Rules Publication Act 1953.
Notified in the Gazette on 24 December 2003
These rules are administered in the Department of Justice and Industrial Relations.